By: Dana Engram
NAD+ and Aging
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is a vital cofactor involved in homeostasis and energy production (Lautrup et al., 2019).
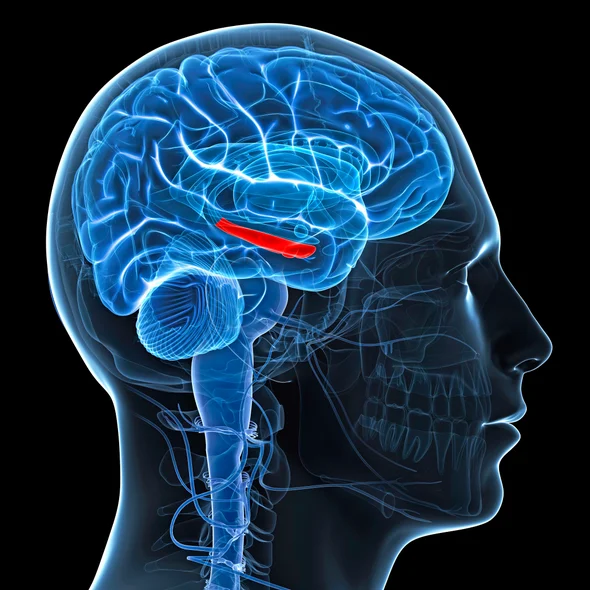
NAD+ production in our body naturally decreases as we age. Why this occurs remains unknown and is still under rigorous experimentation and debate in biochemical research. One of the main areas of the brain that NAD+ is crucial for is the hippocampus, which is a structure in the midbrain responsible for learning and long-term memory. Emerging research studies have discovered that low NAD+ production in the body contributes to almost every known hallmark of aging (Lautrup et al., 2019).
There are 10 major hallmarks of aging that degrade hippocampal regions. The most prominent hallmarks include dysfunction of organelles, compromised immune system, impaired DNA repair, inflammation, broken neural networks, and senescence (Lautrup et al., 2019). All of these malfunctions taken together catalyze the onset of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). This is the reason why, as we age, we may begin to feel symptoms of muscle soreness, more fatigue, stiffness, off balance, slower processing ability, moody behavior, and memory loss.
These adverse symptoms of aging appear to be directly linked to an absence of NAD+ production. Individuals between the age ranges of 50-80 yrs old have a higher chance of having impaired neuronal function (Lautrup et al., 2019), particularly as NAD+ production begins to slow down in the hippocampus. Molecular Gerontologist, Evandro Fang revealed a strong correlation between low NAD+ levels even in premature aging disorders such as Cockayne Syndrome and Ataxia Telangiectasia.
So what is NAD+ and why is it so imperative to a healthy aging process? Growing older is inevitable, so how can we ensure a safe and healthy transition into our elder years? Is the NAD+ molecule the solution to reversing neurodegenerative disorders and restoring the mental and physical health of our elder population? Before we can answer these questions, let’s first dive into the many physiological health effects that NAD+ provides for our nervous system.
What is NAD+
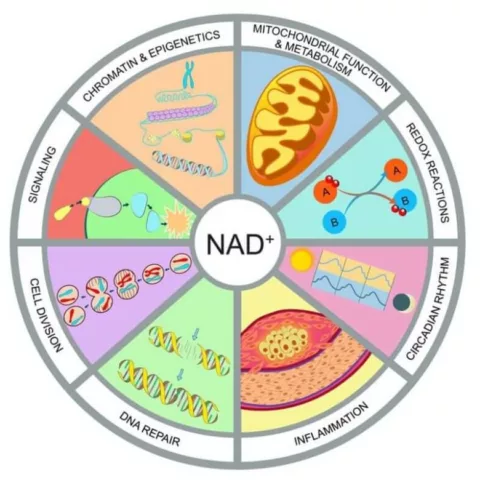
NAD+ is a powerhouse signaling molecule localized in cellular compartments like the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria. It controls hundreds of key cellular processes involving metabolism, DNA repair, circadian rhythms, and immune system response. NAD+ also has many precursor or “parent” molecules that also possess major regenerative and restorative properties. The main precursors include nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferases (NMNAT), and histone deacetylase sirtuins (SIRT) (Lautrup et al., 2019). NMN’s, NMNAT’s, and SIRT’s are proteins found to restore and build new neural connections, promote healthy aging, and build an increased lifespan (Lautrup et al., 2019).
They are also crucial intermediates for roughly 500 key enzymatic reactions (Rajman et al., 2018) including energy production in mitochondria, cellular glycolysis, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) expression, neural progenitor cell proliferation, and stem cell proliferation. Think of NAD+ and their parent molecules as espresso shots for your neurons. It provides the aging brain with enzymatic cofactors necessary for mediating strong cognitive processing.
NAD+ and Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a neurological disorder that typically affects individuals ages 65+. In a nutshell, proteins and their neurons start to become misfolded and then form aggregates outside of the neurons. These aggregates are called amyloid-β-proteins. The disease process begins with the aggregation of amyloid proteins in the form of amyloid plaques (Aβ). Amyloid plaques are highly toxic and progressive growth of Aβ in the brain causes problems with the neuron’s ability to send messages. This leads to memory loss characteristic of AD.
However, recent studies show that NAD+ augmentation can stop these cognitive deficits by swallowing up Aβ plaques and limiting Aβ growth (Gong et al., 2013). NAD+ augmentation enhances synaptic plasticity, promotes the proliferation of neural progenitor cells, and can restore memory in individuals affected by Alzheimer’s (Hou et al., 2018).
Benefits of NAD+ IV Therapy
You may be familiar with daily niacin tablets to help you achieve homeostatic levels of NAD+. However, oral drug administration is one of the most complicated pathways to target tissues because it travels via the GI tract and is absorbed in our portal lymphatic system, at which point the NAD+ concentration is rapidly degraded (Finkel et al., 2009) (Humphrey et al., 2007). And while niacin should be regularly consumed, you may still be missing other crucial NAD+ boosters like NMN’s, SIRT’s, and NMNAT’s that your body requires for optimal cognitive functioning.
This makes an intravenous injection of NAD+ an attractive therapeutic method for the treatment of acute neuronal damage and neurodegenerative diseases (Sinclair et al., 2018). As NAD+ levels decline with age, raising levels to back up to baseline requires an ever-increasing amount of NAD+ and its precursors. IV injection is the fastest and most certain and most controlled way of achieving homeostatic levels of NAD+ through the body and across the blood-brain barrier (Finkel et al., 2009) (Humphrey et al., 2007).
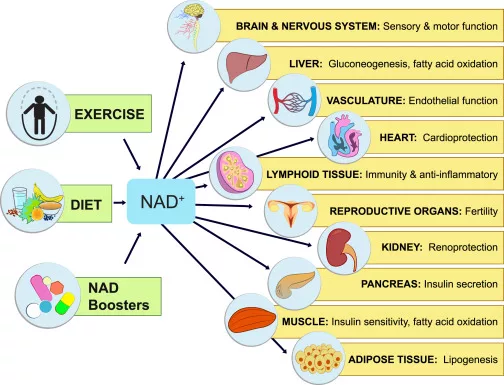
NAD+ IV can give you the energy boost your body needs to repair worn-down connective tissue and sharpen your sensory organs. All in all, this molecule has a plethora of protective mechanisms to support the essential functions of almost every organ system in our body including:
- Increasing fertility
Promotes and extends fertility in males and females.
- Boosting immune system
Regulates immune system function and inflammation by monitoring stress response. 3. Improving pancreatic insulin secretion
Can improve glucose and lipid homeostasis in obese individuals and prevent obesity by repairing glucose production in the liver and insulin secretion in the pancreas.
- Improving vascularity and blood flow
Protects against cardiovascular disease by promoting endothelial and myocardial cell proliferation in post-ischemic hearts.
- Heightening sensory and motor function
Promotes cognitive and sensory function in various structures of the brain involved with learning, memory, balance, and coordination.
- Builds stronger skeletal muscle
Enhances muscle regeneration by increasing the number of quality muscle stem cells. Repairs energy production within muscle fibers that reduces the chances of muscular dystrophy.
The best part is that NAD+ is an all natural and essential supplement for your body.
Contact Us:
If you or a loved one are battling a neurological condition or would like to learn more about how NAD+ IV therapy can help you, Physio Logic has you covered! Take the first step in your journey towards optimal health and wellness, by scheduling a consultation to find out how NAD+ can help you quickly, comfortably, and for the long term. Contact our functional health team at Physio Logic today and start receiving the benefits of NAD+ IV therapy!
409 Fulton Street, 2nd Floor
(Entrance on Willoughby Street)
Brooklyn, NY 11201
p: 718.550.2439
f: 718.260.0072
References:
- Delaby, C., et al. “Overview of the Blood Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: Promises and Challenges.” Revue Neurologique, 10 Nov. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2022.09.003
- Gong, Bing, et al. “Nicotinamide Riboside Restores Cognition through an Upregulation of Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Coactivator 1α Regulated β-Secretase 1 Degradation and Mitochondrial Gene Expression in Alzheimer’s Mouse Models.” Neurobiology of Aging, vol. 34, no. 6, 2013, pp. 1581–1588.,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.12.005
- Hou, Yujun, et al. “NAD + Supplementation Normalizes Key Alzheimer’s Features and DNA Damage Responses in a New AD Mouse Model with Introduced DNA Repair Deficiency.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 115, no. 8, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718819115
- Lautrup, Sofie, et al. “NAD+ in Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders.” Cell Metabolism, vol. 30, no. 4, 2019, pp. 630–655., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.001
- Liu, Dong, et al. “Nicotinamide Forestalls Pathology and Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer Mice: Evidence for Improved Neuronal Bioenergetics and Autophagy Procession.” Neurobiology of Aging, vol. 34, no. 6, 2013, pp. 1564–1580., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.11.020
- MEFANET, Czech and Slovak medical faculties network. “Routes of Drug Administration.” WikiLectures, Mefanet, https://www.wikilectures.eu/w/Routes_of_drug_administration
- Rajman, Luis, et al. “Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The in Vivo Evidence.” Cell Metabolism, vol. 27, no. 3, 2018, pp. 529–547., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.011
- https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/biomolecules/amino-acids-and-proteins1/ v/four-levels-of-protein-structure
- https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/our-brain-uses-a-not-so-instant-replay-to-ma ke-decisions/
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/ataxia-telangiectasia/ 11. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/6122/cockayne-syndrome