Do you or someone you know experience symptoms of urinary urgency, frequency, and/or leakage?
Urinary incontinence can have a significant impact on one’s quality of life secondary to reduced physical activity and psychological distress. It is therefore important for those suffering to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Urinary incontinence is a common disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is defined as the involuntary loss of urine and can have a significant impact on the quality of life for those who experience it. In this article, we will delve into urinary incontinence, its causes, types, diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies. We will also address the emotional and psychological concerns associated with this condition and provide practical tips for living well with urinary incontinence.
Urinary incontinence can affect individuals of all ages, but it is more prevalent in older adults. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of urinary incontinence, including weakened pelvic floor muscles, bladder function abnormalities, and obstructed urinary flow. Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, pregnancy, menopause, and neurological diseases can also increase the risk of urinary incontinence.
There are different types of urinary incontinence, including stress incontinence, urgency incontinence, mixed incontinence, and functional incontinence. Stress incontinence occurs when pressure is exerted on the bladder, such as during coughing or sneezing, and is characterized by the loss of small amounts of urine. Urgency incontinence, on the other hand, is characterized by a sudden and intense urge to urinate, followed by involuntary urine loss. Mixed incontinence combines features of stress incontinence and urgency incontinence, while functional incontinence is related to physical or cognitive impairments that hinder timely access to the bathroom.
The diagnosis of urinary incontinence involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s symptoms, along with a physical examination and additional tests such as urine analysis and urodynamic studies. These tests help determine the specific type of urinary incontinence and rule out other potential underlying causes. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience urinary incontinence, as the appropriate treatment depends on the specific type and cause of the condition.
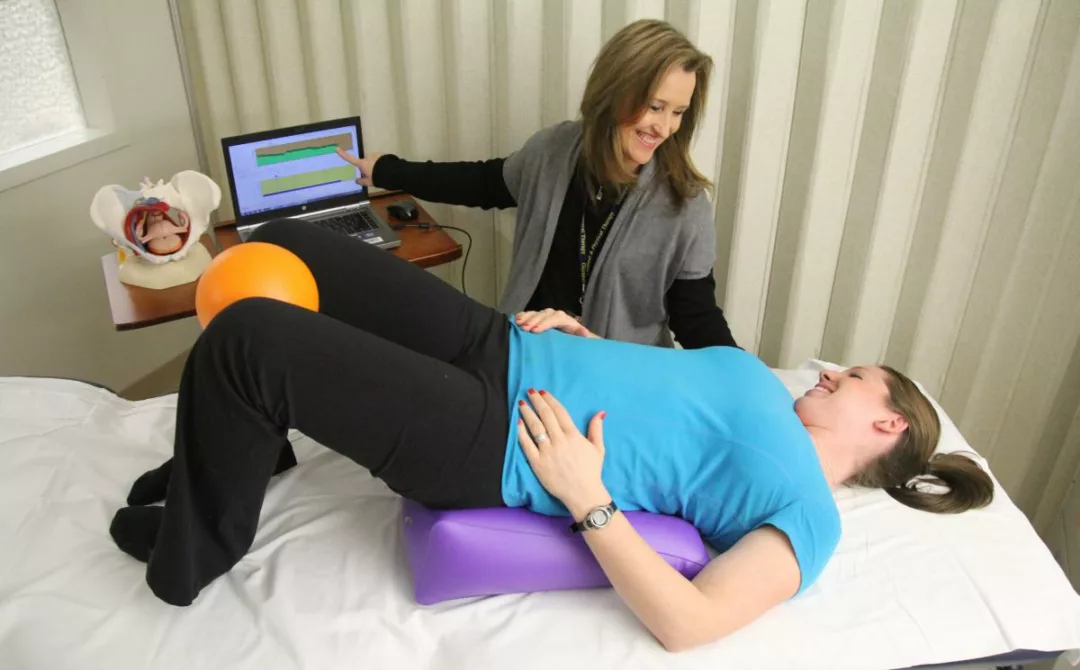
The treatment of urinary incontinence may vary depending on the individual case. For some patients, lifestyle changes and conservative therapies may be sufficient to improve symptoms. These changes may include reducing fluid intake before bedtime, managing caffeine and alcohol consumption, and adopting bladder training techniques and pelvic floor exercises. Pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegel exercises, can strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control.
In more severe cases or when lifestyle changes and conservative therapies are ineffective, other treatment approaches may be considered. These may include the use of medications to control urinary incontinence symptoms, medical devices such as pessaries to support the bladder, or even surgery in certain cases. Surgery may be necessary to correct structural issues that contribute to urinary incontinence, such as pelvic organ prolapse or obstructed urinary flow.
It is important to note that living with urinary incontinence does not have to be limiting. There are many strategies and products available to help manage symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. Absorbent products, such as adult diapers and pads, can provide additional protection and help maintain confidence and comfort during the day and night. Specific hygiene products, such as gentle cleansers and protective creams, can also be used to care for the skin and prevent irritation or infection.
In addition to the physical impact, urinary incontinence can also have a significant emotional and psychological impact. Many individuals feel embarrassed or isolated due to their condition, which can affect self-esteem and personal relationships. It is important to remember that urinary incontinence is not a cause for shame, and seeking support and understanding from family, friends, and healthcare professionals can make a big difference. Support groups and organizations also exist that offer resources and education on urinary incontinence.
In summary, urinary incontinence is a common disorder that can affect the quality of life for those who experience it. However, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies, it is possible to live well with urinary incontinence. If you are experiencing symptoms of urinary incontinence, we recommend seeking medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember that you are not alone, and there are many options available to help you maintain an active and fulfilling life.
Engage in unparalleled care in Physiologic!
In addition to the treatment options mentioned earlier, there are several advanced therapies available for individuals with persistent or severe urinary incontinence. These therapies are typically considered when conservative treatments have been unsuccessful or when the condition significantly impacts a person’s daily life. Some of these advanced therapies include:
- Nerve Stimulation: This involves the use of electrical stimulation to modulate the nerves involved in bladder control. Two common types of nerve stimulation are sacral neuromodulation and posterior tibial nerve stimulation. Sacral neuromodulation uses a surgically implanted device to deliver electrical impulses to the sacral nerves, while posterior tibial nerve stimulation involves the placement of a small electrode near the ankle to stimulate the posterior tibial nerve. These therapies help regulate bladder function and can provide relief for certain types of urinary incontinence.
- Injectable Bulking Agents: Bulking agents, such as collagen or synthetic materials, can be injected into the tissues surrounding the urethra to improve its closure and reduce urine leakage. This procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis and can provide temporary relief for stress urinary incontinence.
- Botulinum Toxin Injections: Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, can be injected into the bladder muscle to help relax the overactive bladder and reduce the frequency of urgency incontinence episodes. This treatment is particularly effective for individuals with urgency incontinence that does not respond to other therapies.
- Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation (PTNS): PTNS involves the placement of a fine needle near the tibial nerve in the ankle and delivering electrical stimulation to modulate the nerves involved in bladder control. This therapy is performed in a healthcare setting and typically requires multiple sessions over several weeks.
It’s important to note that the appropriateness of these advanced therapies varies depending on individual circumstances. A healthcare professional will assess each case and determine the most suitable treatment options based on factors such as the type of urinary incontinence, overall health, and personal preferences.
Aside from medical interventions, there are practical strategies that can help individuals manage urinary incontinence in their daily lives. These include:
- Timed Voiding: Establishing a regular schedule for voiding can help train the bladder and reduce episodes of urgency incontinence. Setting specific times to use the bathroom, even if there is no immediate urge, can help maintain bladder control.
- Fluid Management: While it’s important to stay hydrated, individuals with urinary incontinence may need to monitor their fluid intake, especially before bedtime or during activities that may trigger leakage. Limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption can also help reduce urinary frequency and urgency.
- Absorbent Products: As mentioned earlier, absorbent products such as adult diapers or pads can provide additional protection and help individuals feel more secure and confident during daily activities.
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises: Regularly performing pelvic floor exercises, known as Kegel exercises, can strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control. It’s important to learn proper technique and perform these exercises consistently for optimal results.
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and managing chronic conditions such as diabetes can contribute to better bladder control and overall urinary health.
Remember, every individual’s experience with urinary incontinence is unique, and treatment approaches may vary. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis, guidance on appropriate treatment options, and ongoing support in managing urinary incontinence effectively.
Join Dr. Vivian Zhang and Dr. Eva Shi in a discussion about the different types of urinary incontinence one may experience, the risk factors, and current treatment options.